快速使用
vuex 使用案例 (opens new window)(常规版 ✨)
vuex 模块化应用 (opens new window)(纯模块划分版)
vuex 模块化应用 (opens new window)(命名空间版 ✍)
# 一、基础认知
# 1、Devtools
Vue 的官方调试工具 Devtools (opens new window) (opens new window)已经集成了 Vuex,提供了诸如零配置的 Time-travel 调试、Revert 回退、Commit 提交(会影响 Base State)、状态快照、导入导出等高级调试功能(一定要亲自 ✍ 体验)。如图所示:
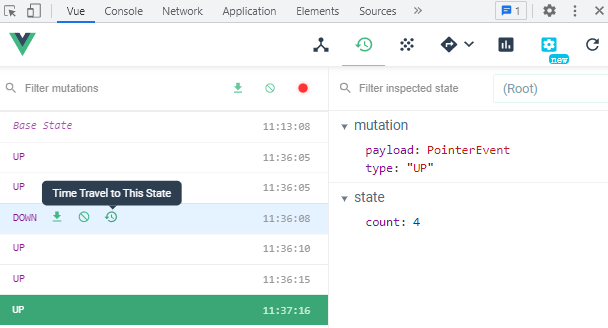
我们可以通过下面的这个小案例,快速入手 vuex 的使用:
# 2、辅助函数
辅助函数返回本质上返回的是一个对象(值为函数),所以我们可以使用拓展运算符...将它们结构出来,和常规 computed 函数放在一起。
提示
辅助函数仅仅是可以简化我们一次性引入多个数据,不是非用不可。有些情况下,使用辅助函数反而带来不便(如:setup 中使用 vuex4)
辅助函数的本质
像我们前面在 Actions、Mutations 中,使用辅助函数就大大简化了我们的操作(帮我们触发 dispatch、commit)
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'AboutWorld',
computed: {
countM: function mappedState() {
return this.$store.state.count
},
storeNumb: function mappedState() {
return this.$store.state.numb
}
},
mounted() {
// 使用辅助函数
const result = mapState({ storeCount: 'count', storeNumb: 'numb' })
// 打印结果:是一个包含计算属性countM的对象(结果和computed🤔效果一样)
console.log(result)
}
}
<script>
import { mapAction, mapMutations, mapGetter, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetter(['doubleCount'])
// ======================
// count() {
// return this.$store.state.count
// }
// doubleCount() {
// return this.$store.getter.doubleCount
// }
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['increment']),
...mapAction(['upAsync'])
// ======================
// increment() {
// this.$store.commit('increment')
// }
// upAsync() {
// this.$store.dispatch('upAsync')
// }
}
}
</script>
# 二、核心概念
# 1、State
其实 State 就没什么说的了,那我们就换个方向,
const state = {
count: 0
}
通常对于 vuex 中的 state,组件中:
- 要么直接使用
this.$store.state - 但有时同一组件中多处要使用同一个 state 的话,就会使用 computed 进行接收即可。
<script>
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
// ...mapState({
// storeCount1: state => state.count1 // 重命名
// storeCount2: count2 // 重命名
// })
// ======================
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
</script>
# 2、Getter
Getter 用于对 Store 中的数据进行加工处理(包装)形成新的数据(简单的说就是 Getter 是 Store 中的计算属性)。
为什么我们不直接使用组件中的计算属性呢?它不一样可以操作 store 数据吗?
答案
因为 getters 可以被任何组件调用,而不局限于当前组件。
const state = {
listArr: [
{ id: 1, name: '华为', product: '手机', hasStock: false},
{ id: 2, name: '小米', product: '家居', hasStock: true },
{ id: 3, name: '格力', product: '空调', hasStock: true}
]
}
const getters = {
titleMsg(state) {
return state.listArr.map((item) => item.name + '--' item.product)
}
// 使用第二个参数
hasStock(state) {
return state.listArr.filter((item) => item.hasStock)
},
stockProd(state, getters) {
return getters.hasStock.map(item => item.product)
}
// 返回回调函数
getProdDetails(state) {
return function(id) {
return state.listArr.find((item) => item.id === id)
}
}
// {{ $store.getters.getProdDetails(2) }} 使用
}
# 3、Mutations
提示
在 vuex 中,更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation
其实在其他地方也可以对 state 进行更改,但作为一种规范:只有在 mutation 中对 state 的修改才会被 Devtools 监控到(这也间接导致 mutation 中只能进行同步操作)
在 Pinia 中就极为简便了,可以直接修改 state,并且还有简写形式:
// store.state.count++
store.count++
关于传参 ✍ 问题
- 问题 1
没有传参时,打印的 payload 为 PointerEvent 对象 🤔,而不是 undefined
const mutations = {
// 方式1
// UP(state, payload = 1) {
// state.count += payload;
// },
// 方式2
UP(state, payload) {
// 一、没有传参时payload的结果
// 1、组件中直接使用commit:PointerEvent对象🤔 --> 真值
// 2、Actions中使用commit:undefined --> 假值
console.log(payload)
// 二、有传参时payload的结果
// 就是传入的内容
console.log(typeof payload)
// console.log(payload instanceof PointerEvent)
if (payload && !(payload instanceof PointerEvent)) {
state.count += Number(payload)
} else {
state.count++
}
}
}
- 问题 2
由于 Vuex 内部使用的是 JSON.stringify() 方法将 mutation 的 payload 序列化为字符串类型,以便于在不同的组件和页面之间传递,所以:
当使用 commit 方法传入一个数字类型的参数时,该参数在触发 mutation 时会自动被转换为字符串类型
<script>
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations(['increment']),
// 使用的时候传递参数即可 @click="changeInfo({index: 0,hasStock: true})"
// ...mapMutations(['changeInfo']),
// ======================
// increment() {
// this.$store.commit('increment')
// }
changeInfo() {
this.$store.commit('changeInfo', {
index: 0,
hasStock: true
})
}
}
}
</script>
const mutations = {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
// 使用第二个参数(payload一般是一个对象)
changeInfo(state, payload) {
state.listArr[payload.index].hasStock = payload.hasStock
}
}
拓展:常量代替 Mutation 事件类型
// mutation-types.js
export const SOME_MUTATION = 'SOME_MUTATION'
// store.js
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import { SOME_MUTATION } from './mutation-types'
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { ... },
mutations: {
// 我们可以使用 ES2015 风格的计算属性命名功能来使用一个常量作为函数名
[SOME_MUTATION] (state) {
// mutate state
}
}
})
# 4、Actions
Mutation 能干的活其实 Actions 也可以干 🤔,并且还可以完成 Mutation 不能完成的异步操作。
但由于 Devtools 子在 Mutations 上监听,所以 Actions 不能直接操作 state 数据(虽然操作也能生效),应该使用commit让 Mutations 去修改 state 数据(大写的卑微:Pinia 中就去掉了 Mutation)。
关于 actions 的 context ✍ 参数
const actions = {
argum(context, value) {
console.log(context) // context可以看做一个miniStore(迷你版的store)
},
// ======================
// 1、完整
demo(context) {
context.dispatch('asyncAction') // 和Getter的第二个参数一样
context.commit('increment') // 修改state
// context.state.count
},
// 2、简写
demo({ dispactch, commit }) {
dispactch('asyncAction')
commit('increment')
// context.state.count
}
}
下面例子中的逻辑处理部分,在原组件中直接写个 methods 不就好了吗,为什么还有搞到 actions 中去
答案
其实,在开发中 action 中写的一些逻辑处理,通常是非常重要或者复用性非常高的内容(而不是像下面一样简单的逻辑),例如:token 的操作、用户名信息操作等
但是异步任务在 actions 中应用(如:ajax 请求)就很多了,详细内容可以看后面 vuex 的模块化部分。
放在 store 的 actions 是可以方便模块化管理数据
const actions = {
// 1、逻辑处理
upIfOddAction({ commit, state }) {
if ((state.count + 1) % 2 === 0) {
commit('increment') // 修改state
}
},
// 2、异步任务
upAsyncAction({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment') // 修改state
resolve('修改state成功了')
}, 2000)
})
}
}
异步任务
const actions = {
// Promise链式调用
login({ commit }, userInfo) {
const { username, password } = userInfo
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
login({ username: username.trim(), password: password })
.then((response) => {
const { data } = response
commit('SET_TOKEN', data.token)
setToken(data.token)
resolve()
})
.catch((error) => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// await/async
async changeRoles({ commit, dispatch }, role) {
const token = role + '-token'
commit('SET_TOKEN', token)
setToken(token)
const { roles } = await dispatch('getInfo')
resetRouter()
// generate accessible routes map based on roles
const accessRoutes = await dispatch('permission/generateRoutes', roles, { root: true })
// dynamically add accessible routes
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes)
// reset visited views and cached views
dispatch('tagsView/delAllViews', null, { root: true })
}
}
<script>
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
// ...mapAction(['upAsyncAction'])
// ======================
upAsyncAction() {
this.$store.dispatch('upAsyncAction').then((res) => {
console.log(res)
})
}
}
}
</script>
开发应用
我遇到的一个 Actions 的经典场景就是:
顶部导航栏点击切换时,不断的重复请求数据(后端监控到了该接口存在大量调用)
解决方案:
在 action 通过 axios 异步获取数据,并触发 Mutation 保存获取的数据供后续使用。
# 三、store 模块化
应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中
简单的说就是放在 store 文件夹内第一梯队的位置。当然如果你的 store 文件太大,只需将 action、mutation 和 getter 分割到单独的文件。
├── store
├── index.js
├── getters.js # 根级别的 getters
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js
└── products.js
# 1、模块划分
Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter。
这样可以防止 store 变得过于臃肿。使用示例:购物车示例 (opens new window)
注意
将 Vuex 的状态管理模块化划分后,state、getters、mutations、actions 都变成了局部的,只能在该模块内部进行访问和修改。
- index.js
import getters from './getters'
import cart from './modules/cart'
import products from './modules/products'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 引入模块
modules: {
cart,
products
},
// 引入根级别getters
getters
})
export default store
# 2、命名空间
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的。
通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
开启命名空间后,我们结合辅助函数,可以实现和非模块化使用时大差不差的体验感。
// ./modules/user.js
export default {
// 开启命名空间
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
# 3、具体使用
State
State 提供唯一的公共数据源,用于存储共享数据。
// 非模块化
// 1、直接
this.$store.state.stateA
// 2、辅助函数
// stateA
...mapState(['stateA','stateB']),
// 模块化(使用了命名空间)
// 1、直接
this.$store.state.模块名1.stateA
// 2、辅助函数
// stateA
...mapState('模块名1', ['stateA','stateB'])
...mapState('模块名2', ['stateC','stateD'])
Getters
Getter 用于对 Store 中的数据进行加工处理(包装)形成新的数据,类似于 vue 中的计算属性。
// 非模块化
// 1、直接
this.$store.getters.getterA
// 2、辅助函数
// getterA
...mapGetters(['getterA','getterB'])
// 模块化(使用了命名空间)
// 1、直接 🤔
this.$store.getters['模块名1/getterA']
// 2、辅助函数
// getterA
...mapGetters('模块名1', ['getterA','getterB'])
...mapGetters('模块名2', ['getterC','getterD'])
Mutations
Mutation 用于变更 Store 中的数据。
// 非模块化
// 1、直接
this.$store.commit('mutationA', payload)
// 2、辅助函数
// mutationA(payload)
...mapMutations(['mutationA','mutationB'])
// 模块化(使用了命名空间)
// 1、直接
this.$store.commit('模块名1/mutationA', payload)
// 2、辅助函数
// mutationA(payload)
...mapMutations('模块名1', ['mutationA','mutationB'])
...mapMutations('模块名2', ['mutationC','mutationD'])
Actions
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
- 若使用 Action 变更数据,需要通过触发 Mutation 的方式间接变更数据
// 非模块化
// 1、直接
this.$store.dispatch('actionA', value)
// 2、辅助函数
// actionA(value)
...mapActions(['actionA','actionB'])
// 模块化(使用了命名空间)
// 1、直接
this.$store.dispatch('模块名1/actionsA', value)
// 2、辅助函数
// actionA(value)
...mapActions('模块名1', ['actionA','actionB'])
...mapActions('模块名2', ['actionC','actionD'])
# 4、拓展:根节点状态
关于 rootState、rootGetters 使用 ✍
- Getters 中
对于模块内部的 getter,根节点状态会作为其他参数暴露出来
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
// ...
getters: {
sumWithRootCount(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return state.count + rootState.rootCount
}
}
}
- Actions 中
打印 Actions 中的 content 参数时,发现它也是一个包含:commit、dispatch、state、rootState、getters、rootGetters 的对象。
在mutations 中不能直接使用 rootState,因为 mutations 只能修改 state 中的数据,而不能访问其他模块的状态。
解决方案: 使用{ root: true }
一句话,mutation 想要使用 rootState,必须走官方 Vuex 示意图的路线(通过 Actions 转发使用 Mutations 的方式),而不能直接在组件中使用 Mutations
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
// ...
actions: {
someAction({ commit, dispatch, state, rootGetter }) {
commit('increment') // -> 'moduleA/increment' 使用局部的UP
// null:表示传递是数据
// {root:true} 表示使用的是根store中的mutation
commit('increment', null, { root: true }) // -> 'increment' 使用全局的increment
}
}
}
# 三、持久化存储
现象:
在 F5 刷新页面后,vuex 会重新更新 state,所以,存储的数据会丢失。
# 1、常规解决方案
- store.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
// Vuex中的数据
state: {
token: sessionStorage.getItem('newToken'),
userInfo: JSON.parse(sessionStorage.getItem('newUserInfo') || '[]')
},
mutations: {
// 登录成功后的token值
setToken(state, newToken) {
state.token = newToken
sessionStorage.setItem('newToken', newToken)
},
// 用于存储获取的用户信息
setUserInfo(state, newUserInfo) {
state.userInfo = newUserInfo
sessionStorage.setItem('newUserInfo', JSON.stringify(newUserInfo))
}
}
})
- 退出登录时
menu_loginout(){
// 1、清除sessionStorage中的数据
// 要么:(大量数据时)
sessionStorage.clear()
// 或者:(少量数据时)
this.$store.commit('setToken','')
this.$store.commit('setUserInfo','')
// 2、删除vuex中的数据(F11刷新)
window.location.reload()
this.$router.push('/login')
}
# 2、使用 vuex-persistedstate
利用vuex-persistedstate (opens new window)插件自动实现持久化存储。
版本选择:
vuex-persistedstate@3.2.1(默认最新版是配合 vue3 使用)
- 简单示例:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 1、导入包
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
// ...
// 2、使用插件
plugins: [createPersistedState()]
})
- 插件配置(下面演示的全部为默认值:可省略 👀):
/* vuex数据持久化配置 */
plugins: [
createPersistedState({
// 1、存储方式:localStorage、sessionStorage、cookies
storage: window.localStorage,
// 2、存储的 key 的key值
key: 'vuex',
path: []
// 3、指定需要持久化存储state
render(state) {
return { ...state } // 默认存储了state中所有的数据(es6扩展运算符)
}
})
]
← vuex基础 【axios请求封装✨】 →
